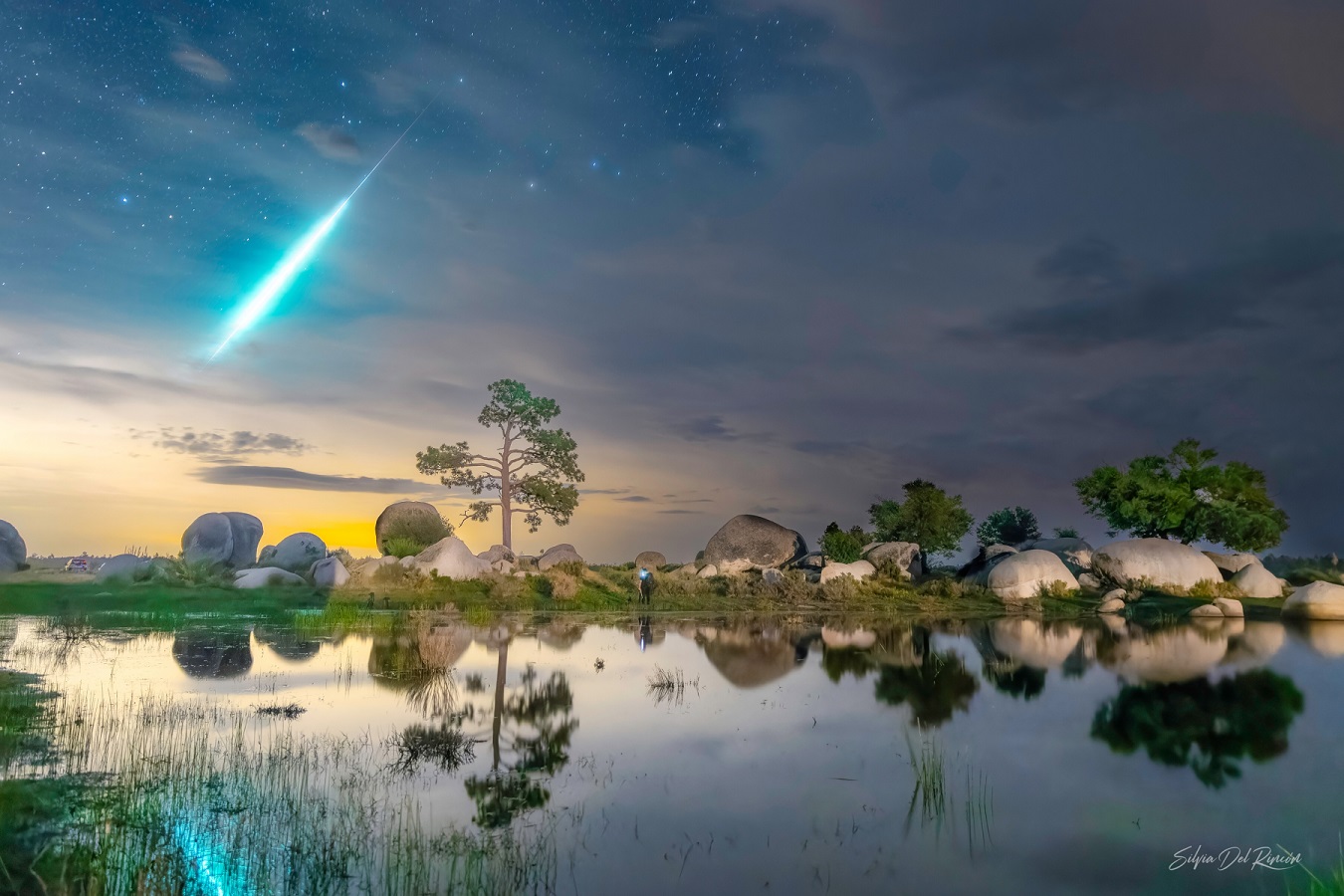
Silvia Del Rincón captured this colorful fireball on July 23, 2023, at 01:53 PDT (8:53 UT) from Juárez, Baja California Norte, Mexico. This is the same fantastic event that was displayed in last week’s article. ©Silvia Del Rincón
Silvia Del Rincón captured this colorful fireball on July 23, 2023, at 01:53 PDT (8:53 UT) from Juárez, Baja California Norte, Mexico. This is the same fantastic event that was displayed in last week’s article. ©Silvia Del RincónDuring this period, the moon reaches its full phase on Tuesday December 26th. On that night the moon will lie opposite the sun and will lie above the horizon all night long. This weekend the waxing gibbous moon will set during the early morning hours, leaving only a couple of hours between moon set and dawn free of interfering moonlight. The estimated total hourly rates for evening observers this weekend should be near 3 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 2 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S) For morning observers, the estimated total hourly rates should be near 13 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 9 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S). The actual rates seen will also depend on factors such as personal light and motion perception, local weather conditions, alertness, and experience in watching meteor activity. Rates are reduced due to moonlight. Note that the hourly rates listed below are estimates as viewed from dark sky sites away from urban light sources. Observers viewing from urban areas will see less activity as only the brighter meteors will be visible from such locations.
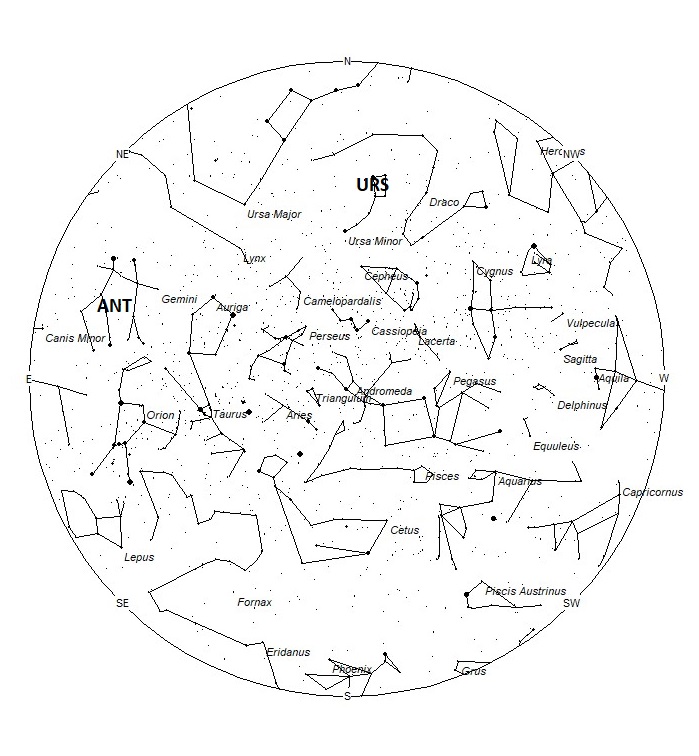
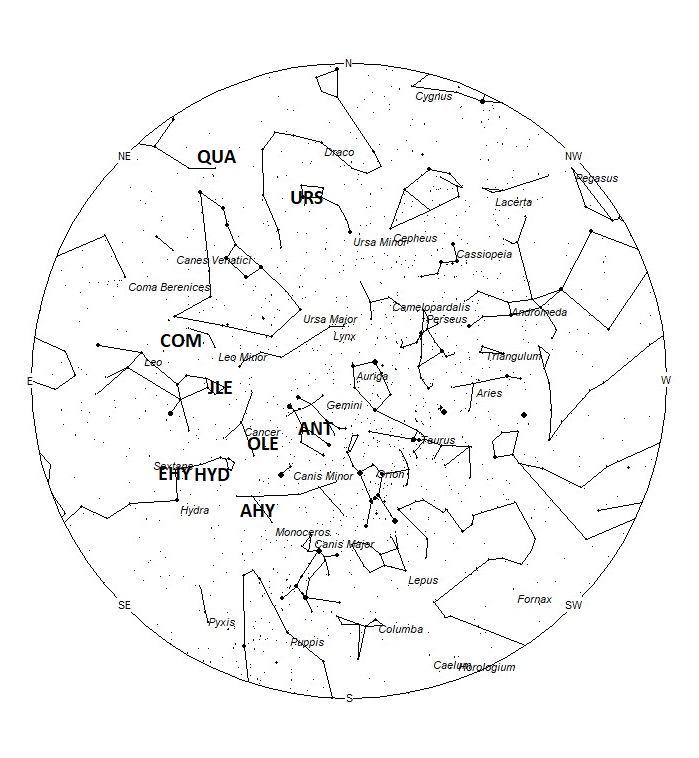
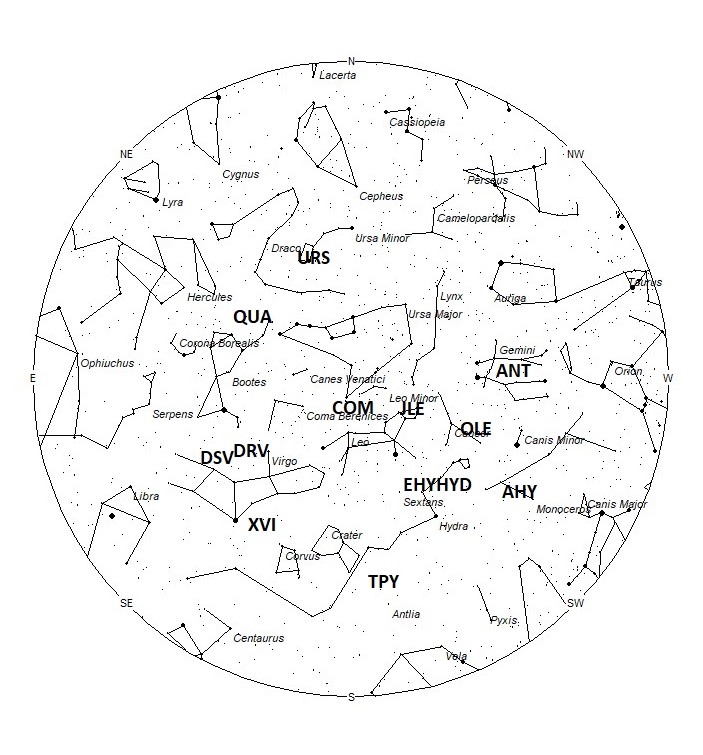
The radiant (the area of the sky where meteors appear to shoot from) positions and rates listed below are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning December 23/24. These positions do not change greatly day to day so the listed coordinates may be used during this entire period. Most star atlases (available at science stores and planetariums) will provide maps with grid lines of the celestial coordinates so that you may find out exactly where these positions are located in the sky. I have also included charts of the sky that display the radiant positions for evening, midnight, and morning. The center of each chart is the sky directly overhead at the appropriate hour. These charts are oriented for facing south but can be used for any direction by rotating the charts to the desired direction. A planisphere or computer planetarium program is also useful in showing the sky at any time of night on any date of the year. Activity from each radiant is best seen when it is positioned highest in the sky, either due north or south along the meridian, depending on your latitude. Radiants that rise after midnight will not reach their highest point in the sky until daylight. For these radiants, it is best to view them during the last few hours before dawn. It must be remembered that meteor activity is rarely seen at its radiant position. Rather they shoot outwards from the radiant, so it is best to center your field of view so that the radiant lies toward the edge and not the center. Viewing there will allow you to easily trace the path of each meteor back to the radiant (if it is a shower member) or in another direction if it is sporadic. Meteor activity is not seen from radiants that are located far below the horizon. The positions below are listed in a west to east manner in order of right ascension (celestial longitude). The positions listed first are located further west therefore are accessible earlier in the night while those listed further down the list rise later in the night.
These sources of meteoric activity are expected to be active this week
.
Now that the activity from particles produced by comet 2P/Encke have ceased encountering the Earth, the Taurid showers for 2023 are over and we resume reporting activity from the Anthelion (ANT) radiant. This is not a true radiant, but rather activity caused by the Earth’s motion through space. As the Earth revolves around the sun it encounters particles orbiting in a pro-grade motion that are approaching their perihelion point. They all appear to be radiating from an area near the opposition point of the sun, hence the name Anthelion. These were once recorded as separate showers throughout the year, but it is now suggested to bin them into a category separate from true showers and sporadics. This radiant is a very large oval some thirty degrees wide by fifteen degrees high. Activity from this radiant can appear from more than one constellation. The position listed here is for the center of the radiant which is currently located at 07:00 (105) +23. This position lies in central Gemini, 4 degrees southeast of the 3rd magnitude star known as Mebsuta (epsilon Geminorum). This radiant is best placed near 01:00 local standard time (LST) when it lies on the meridian and is highest in the northern sky. Rates at this time should be near 2 per hour as seen from the northern hemisphere and 1 per hour as seen from south of the equator. With an entry velocity of 30 km/sec., the average Anthelion meteor would be of slow velocity.
The alpha Hydrids (AHY) were discovered by Dr. Peter Brown and are mentioned in his article “A meteoroid stream survey using the Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar”. This shower is active from December 15 through January 22 with maximum activity occurring on January 6th. The radiant is currently located at 07:58 (120) -06. This position lies in eastern Monoceros, 4 degrees southwest of the 4th magnitude star known as zeta Monocerotis. These meteors are best seen near 0200 LST when the radiant lies highest above the northern horizon. At 45 km/sec. the alpha Hydrids produce meteors of medium velocity. Expected rates this week are less than 1 per hour no matter your location.
The Volantids (VOL) are a weak shower active from December 27 through January 4. They are best known for outbursts of activity near the new year. On December 31st, the radiant is located at 08:02 (121) -72. This position lies in central Volans, 4 degrees south of the 4th magnitude star known as epsilon Volantis. These meteors are not visible north of 20 N latitude. These meteors are best seen near 0200 LST when the radiant lies highest above the southern horizon. At 28 km/sec. the Volantids produce meteors of medium-slow velocity. Expected rates this week are less than 1 per hour no matter your location.
The Omicron Leonids (OLE) were also discovered by Damir Šegon and the Croatian Meteor Network team based on studying SonotaCo and CMN observations (SonotaCo 2007-2011, CMN 2007-2010). These meteors are active from December 20 through January 22. Maximum activity occurs on January 10th. The radiant is currently located at 08:07 (122) +11. This position lies in southwestern Cancer, 2 degrees northwest of the 4th magnitude star known as Tarf (beta Cancri). These meteors are best seen near 0200 LST when the radiant lies highest above the northern horizon. At 39 km/sec. the omicron Leonids produce meteors of medium velocity. Expected rates this week are less than 1 per hour no matter your location.
The sigma Hydrids (HYD) are active from a radiant located at 09:13 (138) -01. This area of the sky is located in western Hydra, 3 degrees south of the 4th magnitude star known as theta hydrae. These meteors are active from November 24 through January 7th, with the main maximum activity occurring on December 7th. To best see these meteors, face toward the north during the last couple of hours prior to dawn. With an entry velocity of 58km/sec, most of these meteors would appear swift. Expect to see less than 1 per hour no matter your location.
The C Velids (CVE) is a continuation of the Puppid/Velid activity this time of year. Unlike the two-week activity during the first half of December, the C Velids are only active on 6 nights centered on December 28th. This segment of the Puppid/Velids is not as strong as the previous one and rates are low, even at maximum activity. At maximum, the radiant is located at 09:20 (140) -54. This area of the sky lies in southern Vela, 2 degrees north of the 2nd magnitude star known as Markeb (kappa Velorum). These meteors are best seen near 0400 LST when the radiant lies highest above the southern horizon. At 39 km/sec. the C Velids produce meteors of medium velocity. Like all sources of the Puppid/Velid complex, these meteors are not well seen from the northern hemisphere. They are best seen from the deep southern hemisphere where the sources are found high in the sky during the southern summer mornings. Activity from this complex is weak in January with barely discernible radiants in Carina and Crux. Activity increases in February with several radiants spread across Centaurus. This complex weakens again in March with the last traces appearing in the Lupus/Norma region of the sky.
The January Leonids (JLE) were discovered by Dr. Peter Brown and are mentioned in the same publication as the Alpha Hydrids. This shower is active from December 28 through January 07 with maximum activity occurring on January 3rd. The radiant is currently located at 09:23 (141) +27. This position lies in northwestern Leo, 1 degree north of the 4th magnitude star known as Al Min’ħar al A’sad (kappa Leonis). These meteors are best seen near 0300 LST when the radiant lies highest above the northern horizon. At 52 km/sec. the January Leonids produce meteors of swift velocity. Expected rates this week are less than 1 no matter your location.
The eta Hydrids (EHY) were recently discovered by members of the Croatian Meteor Network. This radiant is active from November 26 through January 1st with maximum activity occurring on December 12th. The radiant is currently located at 09:40 (145) -01, which places it in western Hydra, near the spot occupied by the 4th magnitude star known as iota Hydrae. This position is close to that of the sigma Hydrids so care must be taken to separate the two sources. These meteors are best seen near 0400 LST when the radiant lies highest above the northern horizon. Current rates should be less than 1 per hour no matter your location. With an entry velocity of 61 km/sec., most activity from this radiant would be of swift speed.
The theta Pyxidids (TPY) consists of two weak showers that peak two weeks apart. The later version is active from December 8 through January 8, with maximum occurring on December 18th. The radiant is currently located at 10:38 (160) -26. This area of the sky is located in southwestern Hydra, 5 degrees northeast of the 4th magnitude star known as alpha Antliae. These meteors are best seen near 0500 LST when the radiant lies nearly overhead. Rates are expected to be less than 1 no matter your location. At 63 km/sec. the theta Pyxids would produce mostly swift meteors.
The Comae Berenicids (COM) are a long duration shower active from December 5th through February 4th. Maximum activity occurs on December 16th. The radiant is currently located at 11:00 (165) +29, which places it in eastern Leo Minor, 4 degrees southwest of the 3rd magnitude star known as Alula Borealis (nu Ursae Majoris). These meteors would be best seen near 05:00 LST, when the radiant lies highest in the eastern sky. Current rates should be near 1 per hour as seen from the northern hemisphere and less than one as seen from south of the equator. At 63km/sec., these meteors would produce mostly swift meteors.
The December chi Virginids (XVI) was discovered by Japanese observers using data from SonotaCo. This source is active from November 26 through December 30 with maximum occurring on December 12th. The radiant is currently located at 13:10 (197) -14, which places it in southern Virgo, 3 degrees southwest of the 1st magnitude star known as Spica (alpha Virginis). Hourly rates should be less than 1 no matter your location. These meteors are best seen during the last dark hour before dawn, when the radiant lies highest above the eastern horizon in a dark sky. At 69 km/sec. the December chi Virginids would produce mostly swift meteors.
The December rho Virginids (DRV) are active from November 29 through December 22 with peak rates occurring near December 5th. The current radiant location is at 13:29 (202) +11, which places it in northern Virgo, 4 degrees east of the 3rd magnitude star known as Vindemiatrix (epsilon Virginis). Current hourly rates would be less than 1 no matter your location. These meteors are best seen during the last dark hour before dawn, when the radiant lies highest above the eastern horizon in a dark sky. At 67 km/sec. the December rho Virginids would produce mostly swift meteors.
The December sigma Virginids (DSV) is a source of long duration discovered by John Greaves using the data from SonotaCo. This source is active from November 26 through January 24 with peak rates occurring near December 21st. The current radiant location is at 13:55 (209) +04, which places it in northern Virgo, 3 degrees northwest of the 4th magnitude star known as tau Virginis. Current hourly rates would be less than 1 no matter your location. These meteors are best seen during the last dark hour before dawn, when the radiant lies highest above the eastern horizon in a dark sky. At 66 km/sec. the December Sigma Virginids would produce mostly swift meteors.
The Quadrantids (QUA) are active from December 26th through January 16th. Maximum occurs on January 4th. The radiant is currently located at 14:44 (221) +50. This position lies in northern Bootes, 3 degrees southeast of the 4th magnitude star known as Asellus Primus (theta Bootis). These meteors are best seen during the last hour before dawn when the radiant lies highest above the northern horizon in a dark sky. At 41 km/sec. the Quadrantids produce meteors of moderate velocity. These meteors are visible from the southern tropics but not seen from the deep southern hemisphere. Current rates would be less than 1 per hour no matter your location.
The Ursids (URS) are active from a radiant located at 14:50 (223) +75. This area of the sky is located in southern Ursa Minor, 1 degree north of the 2nd magnitude star known as Kochab (beta Ursae Minoris). The Ursids are active from December 13-24, with maximum activity occurring on the 22nd. Current rates are expected to be less than 1 per hour. At 33km/sec., these meteors are of medium velocity. Due to the high northern location, these meteors are not visible from the southern hemisphere.
Sporadic meteors are those meteors that cannot be associated with any known meteor shower. All meteor showers are evolving and disperse over time to the point where they are no longer recognizable. Away from the peaks of the major annual showers, these sporadic meteors make up the bulk of the activity seen each night. As seen from the mid-Northern Hemisphere (45N) one would expect to see during this period approximately 10 sporadic meteors per hour during the last hour before dawn as seen from rural observing sites. Evening rates would be near 2 per hour. As seen from the tropical Southern latitudes (25S), morning rates would be near 8 per hour as seen from rural observing sites and 1 per hour during the evening hours. Locations between these two extremes would see activity between these listed figures. Rates are reduced due to moonlight.
You can keep track of the activity of these meteor showers as well as those beyond the limits of visual observing by visiting the NASA Meteor Shower Portal. You can move the sky globe to see different areas of the sky. Colored dots indicate shower meteors while white dots indicate sporadic (random) activity. The large orange disk indicates the position of the sun so little activity will be seen in that area of the sky.
The list below offers the information in tabular form of the showers that I feel are within reach of the visual observer to discern. Hourly rates are often less than 1 but noting parameters such as the duration, radiant distance and the elevation of each meteor, one can compute the probability of shower association. Most showers discovered by video means have rates less than 1 meteor per night away from maximum, so the showers listed in these articles are not as weak as they seem. Rates and positions are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning.
| SHOWER | DATE OF MAXIMUM ACTIVITY | CELESTIAL POSITION | ENTRY VELOCITY | CULMINATION | HOURLY RATE | CLASS |
| RA (RA in Deg.) DEC | Km/Sec | Local Standard Time | North-South | |||
| Anthelions (ANT) | – | 07:00 (105) +23 | 30 | 01:00 | 2 -1 | II |
| alpha Hydrids (AHY) | Jan 06 | 07:58 (120) -06 | 45 | 02:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
| Volantids (VOL) | Dec 31 | 08:02 (121) -72 | 28 | 02:00 | <1 – <1 | III |
| Omicron Leonids (OLE) | Jan 10 | 08:07 (122) +11 | 39 | 02:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
| sigma Hydrids (HYD) | Dec 07 | 09:13 (138) -01 | 58 | 03:00 | <1 – <1 | II |
| eta Hydrids (EHY) | Dec 12 | 09:40 (145) -01 | 61 | 04:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
| theta Pyxidids (TPY) | Dec 18 | 10:38 (160) -26 | 63 | 05:00 | <1- <1 | IV |
| Comae Berenicids (COM) | Dec 16 | 11:00 (165) +29 | 63 | 05:00 | 1- <1 | II |
| December chi Virginids (XVI) | Dec 12 | 13:10 (197) -14 | 69 | 07:00 | <1- <1 | IV |
| December rho Virginids (DRV) | Dec 05 | 13:29 (202) +11 | 67 | 07:00 | <1- <1 | IV |
| December sigma Virginids (DSV) | Dec 21 | 13:55 (209) +04 | 66 | 08:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
| Quadrantids (QUA) | Jan 04 | 14:44 (221) +50 | 41 | 09:00 | <1 – <1 | I |
| Ursids (URS) | Dec 22 | 14:50 (223) +75 | 33 | 09:00 | <1 – <1 | I |
Class Explanation: A scale to group meteor showers by their intensity:
- Class I: the strongest annual showers with Zenith Hourly Rates normally ten or better.
- Class II: reliable minor showers with ZHR’s normally two to ten.
- Class III: showers that do not provide annual activity. These showers are rarely active yet have the potential to produce a major display on occasion.
- Class IV: weak minor showers with ZHR’s rarely exceeding two. The study of these showers is best left to experienced observers who use plotting and angular velocity estimates to determine shower association. These weak showers are also good targets for video and photographic work. Observers with less experience are urged to limit their shower associations to showers with a rating of I to III.
 American Meteor Society
American Meteor Society